Every day, companies of all sizes face a growing number of cyber threats: ransomware, DoS, data leaks, and more. While some cyberattacks are carefully planned and highly targeted (particularly in the context of cyberwarfare or politically motivated campaigns) the majority are opportunistic in nature. Most attackers are not seeking out specific companies but instead scanning broadly for any exposed vulnerabilities they can exploit. This means that even organizations that believe they are not likely targets can still fall victim simply because an opportunity presents itself. In today’s threat landscape, being unprepared is often enough to become a target.
That’s where cyber threat intelligence (CTI) comes in.
CTI helps organizations understand who is potentially targeting them, how attacks are carried out, and what can be done to prevent them. It’s about turning raw data into actionable insights—and it’s the foundation of modern, proactive cyber defense.
At Sling, CTI isn’t just a feature. It’s the core engine behind our risk detection, driven by a massive data lake that continuously collects and analyzes threat signals from the darkest corners of the web.
CTI Explained
Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) is the process of collecting, analyzing, and using information about potential or current threats to protect digital systems. It goes beyond basic data collection. CTI transforms raw threat data into insights that security teams can act on.
CTI typically includes:
- Indicators of Compromise (IOCs): IP addresses, malware hashes, URLs
- Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs): How attackers operate
- Threat actor profiles: Motives, capabilities, and targets
- Operations, incidents: events and intention of carrying out attacks
Unlike traditional cybersecurity approaches that react to threats, CTI is proactive, it helps organizations anticipate, detect, and respond faster.
Here’s a quick breakdown of the types of threat intelligence often used:
| Type | Description | Common Use Case |
| Strategic | High-level trends, long-term risks | CISO briefings, board reports |
| Tactical | Attacker behaviors and TTPs | Threat hunting, blue team ops |
| Operational | Specific campaign-level insights | Ongoing incident investigations |
| Technical | Raw technical data (e.g., IOCs) | Automated detection systems |
By integrating CTI, organizations stay ahead of attackers, often detecting early signs of compromise before any real damage occurs.
Why Cyber Threat Intelligence Matters Today
Today’s cyber threat landscape is broader, faster, and more unpredictable than ever. From ransomware gangs to state-sponsored espionage groups, attackers are constantly adapting their methods.
Key reasons why CTI matters:
- Threats are evolving rapidly: New vulnerabilities and attack techniques appear daily.
- External attack surfaces are expanding: Cloud services, remote work, and third-party vendors increase exposure.
- Attackers are organized: Cybercriminals operate like businesses, using toolkits and sharing data across dark web forums and other communication platforms.
- Security teams are overwhelmed: SOC analysts face high alert volumes and limited resources.
CTI addresses these challenges by:
- Prioritizing real threats over noise
- Accelerating response time with contextual intelligence
- Reducing risk through informed decision-making
For example, a financial firm using CTI might detect that credentials from one of its vendors are being sold on a dark web forum—before the vendor even realizes there’s a breach.In short, CTI turns unknowns into knowns, enabling a smarter, faster, and more focused cybersecurity posture.
The Cyber Threat Intelligence Lifecycle
Cyber threat intelligence isn’t a one-time report—it’s a continuous process. Organizations follow a structured lifecycle to ensure the intelligence they produce is relevant, timely, and actionable.
Below is an overview of the six stages of the CTI lifecycle:
1. Direction
This is where goals are defined. What threats are we trying to understand? Which assets are most at risk? Clear objectives guide the entire intelligence process.
2. Collection
Raw data is gathered from diverse sources such as:
- Open-source intelligence (OSINT)
- Darknet and deep web forums
- Instant messaging platforms
- Malware repositories
- Internal logs and telemetry
3. Processing
The collected data is filtered, cleaned, and normalized. For example, irrelevant or duplicate entries are removed, and indicators are enriched with context.
4. Analysis
Analysts interpret the processed data to uncover patterns, behaviors, and trends. This step transforms raw data into meaningful insights.
5. Dissemination
Findings are delivered to the relevant stakeholders—whether that’s a CISO, SOC team, or automated detection system.
6. Feedback
Stakeholders provide input on how useful the intelligence was. This helps refine the process and improve future output.
Key Benefits of Cyber Threat Intelligence
Cyber threat intelligence is not just about collecting data—it’s about making security smarter, faster, and more aligned with business risk. When implemented effectively, CTI offers significant advantages across the organization.
- Faster Detection and Response
CTI helps security teams recognize threats early—sometimes before they reach the network. This leads to quicker containment and less damage. - Contextual Alert Prioritization
Instead of drowning in alerts, SOCs can focus on what matters. CTI enriches alerts with context like attacker motive, exploit type, and business impact. - Understanding Attacker Behavior (TTPs)
By studying how attackers operate, defenders can anticipate next steps, detect patterns, and harden defenses accordingly. - Improved Vulnerability Management
CTI identifies which vulnerabilities are being actively exploited in the wild—helping teams prioritize patching based on real-world threat activity, not just CVSS scores. - Empowered Decision-Making for Executives
CISOs and boards can make informed security investments based on relevant threat trends and risk intelligence.
Example Use Cases
| Use Case | How CTI Helps |
| Ransomware Defense | Tracks emerging ransomware groups and TTPs |
| Third-Party Risk Assessment | Identifies breaches or leaks involving vendors |
| Incident Response Planning | Provides IOCs and campaign context |
| Threat Hunting | Guides searches with up-to-date adversary profiles |
| Regulatory Compliance (e.g., DORA, NIS2) | Supports threat-based risk assessments |
By offering these advantages, CTI enables a shift from reactive defense to a proactive cybersecurity strategy.
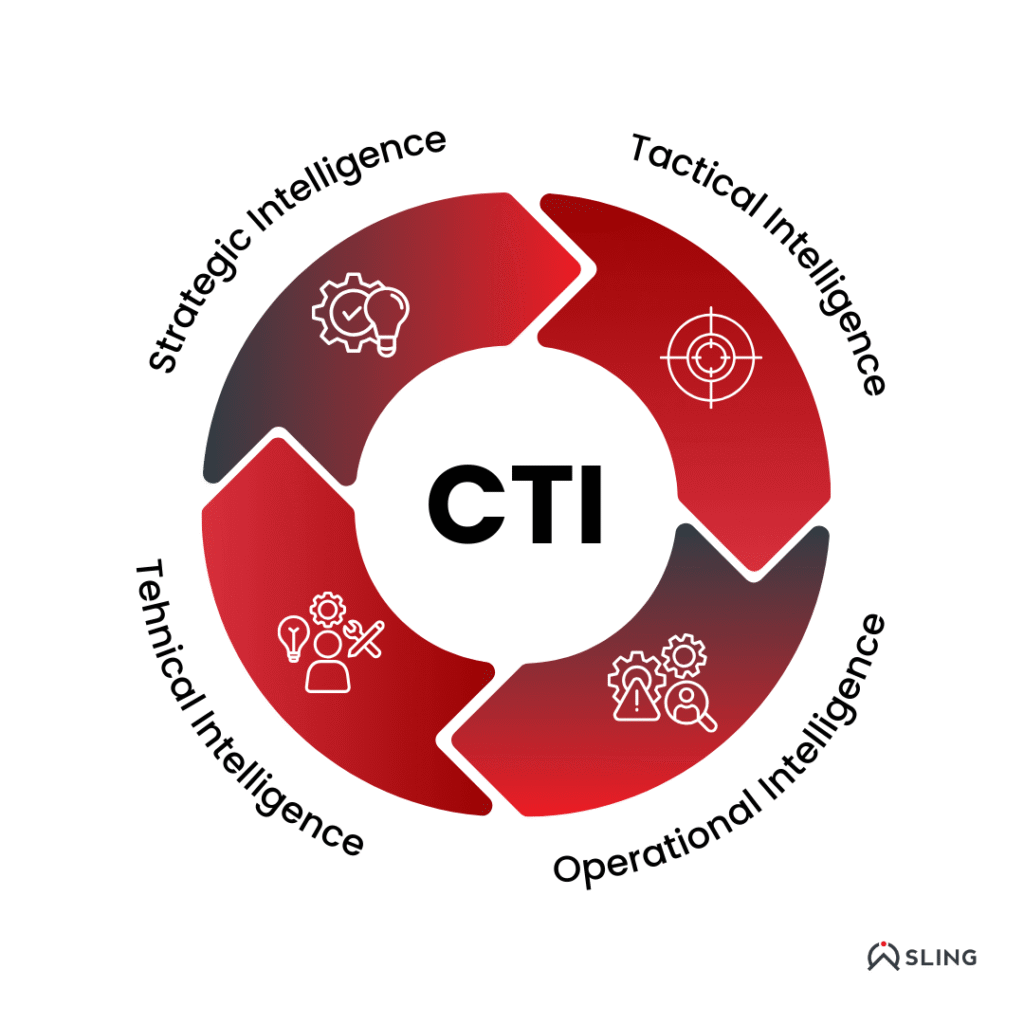
Types of Cyber Threat Intelligence
Not all cyber threat intelligence is created equal. Different types of CTI serve different stakeholders, from executives to SOC analysts, each requiring a specific level of detail and focus.
Here’s a breakdown of the four main types of cyber threat intelligence:
Strategic Intelligence
- Audience: Executives, board members, risk managers
- Focus: High-level insights about long-term trends, threat actor motivations, and geopolitical risks
- Use Case: Guides business and investment decisions in cybersecurity
- Example: “Ransomware targeting healthcare expected to rise in Q4 due to regulatory deadlines”
Tactical Intelligence
- Audience: Security operations centers (SOCs), blue teams
- Focus: Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs) of attackers
- Use Case: Improves detection and response capabilities
- Example: “Group X is known for spear phishing emails followed by Cobalt Strike payloads”
Operational Intelligence
- Audience: Incident response and threat hunting teams
- Focus: Campaign-level insights and current attack infrastructure
- Use Case: Responding to ongoing incidents or anticipating specific attacks
- Example: “This malware campaign is exploiting CVE-2023-XXXXX to gain remote access”
Technical Intelligence
- Audience: Automated tools, threat detection systems
- Focus: Raw, low-level indicators like IPs, file hashes, domain names
- Use Case: Feeds firewalls, SIEMs, and EDR tools for automated blocking
Example: “Blocklist of 50 malicious IPs used in recent phishing campaign”
How Sling Stands Out: CTI at Scale
Most threat intelligence platforms provide fragmented data feeds or rely on narrow sets of sources. Sling takes a fundamentally different approach, by having one of the largest cyber threat intelligence data lakes in the industry, designed to support real-time, actionable insights at scale.
What Powers Sling’s CTI?
- Billions of data points collected from the surface web, deep web, and darknet
- Real-time monitoring of threat actor chatter, marketplaces, and data leaks
- Proprietary crawling technology scanning thousands of closed forums and breach dumps
How Sling Uses CTI to Reduce Risk
- External Attack Surface Monitoring
Sling continuously maps your organization’s online presence—including vendor infrastructure—to detect exposures before attackers do. - Risk Scoring via Sling Score
Each threat is prioritized using a unique scoring engine that weighs severity, likelihood, and potential impact. - Darknet & Deep Web Coverage
Sling dives into hacker forums, Telegram groups, breach marketplaces, and ransomware leak sites to identify emerging threats. - Automated Intelligence Classification
Threat data is structured and ranked automatically using AI-powered models for faster decision-making.
By harnessing CTI at scale, Sling gives security teams the power to move faster than attackers, with visibility far beyond their own perimeter.
As cyber threats grow more sophisticated and targeted, relying solely on traditional defenses is no longer enough. Cyber threat intelligence empowers organizations to move from reactive to proactive, anticipating risks before they escalate.
Whether you’re a global enterprise or a lean security team, CTI helps you:
- Understand your unique threat landscape
- Prioritize risks that matter most
- Strengthen detection and response workflows
- Align security actions with business goals
If you’re ready to gain clarity, reduce noise, and act on the threats that truly matter, Sling is built for you.



